动物实验种类千千万,C57BL/6小鼠可谓是天赋异禀,是非常全能的实验动物品系了!相信大家应该都不陌生,C57BL/6小鼠起源较早且优势明显,一直被研究者青睐。
1921 年 C.C.Little 培育成 C57,并将毛色呈黑色的进行固定培育为 C57BL。1937 年 Little 将维持的第六组亚系定名为 C57BL/6,自此,C57BL/6小鼠诞生啦!
今天要跟大家分享关于C57BL/6小鼠的前世今生。来来来,我们一起敲黑板、划重点啦!

C57BL/6小鼠在科学研究中的应用十分广泛,主要应用在以下几个方面:
在代谢实验中,C57BL/6背景小鼠可用于诱导肥胖(DIO)、非酒精性脂肪性肝炎(NASH)、糖尿病及动脉粥样硬化等模型。目前,维通利华的DIO和NASH模型均有现货,极大地节省了科研工作者诱导模型的时间,加速科研计划的进程。


在老龄化研究中,C57BL/6也是妥妥的明星鼠。为了满足国内研究者对大月龄鼠或老龄鼠的需求,维通利华启动老龄鼠项目——专有空间饲养、专业人员护理、动物福利保障、定期健康监测,可提供不同月龄的VAF/SPF 级别的C57BL/6JNifdc和C57BL/6NCrl小鼠,助力相关研究。
在肿瘤研究领域已有多种C57BL/6背景细胞系,包括肺癌、黑色素瘤、卵巢癌、胰腺癌等,这为肿瘤研究提供了很好的工具。在神经和行为学实验中,C57BL/6小鼠由于酒精偏嗜,可用于成瘾实验;同时也可用于学习、神经退行性疾病、焦虑等行为学研究。
在基因工程鼠领域,C57BL/6小鼠也是佼佼者。上世纪 80 年代末期ES 基因打靶技术崛起,第一个基因敲除鼠选用的背景鼠就是 C57BL/6 。并且C57BL/6N小鼠是国际敲除小鼠联盟(IKMC) 选用的标准背景品系,可谓是基因工程鼠的“始祖”。
随着基因测序的发展,在2002 年首次公开了 C57BL/6 小鼠的基因组序列[1],并将其作为其他小鼠序列的索引参考。因此,C57BL/6也是第一个完成基因测序的小鼠品系。
C57BL/6小鼠用途之广泛,堪称“全能选手”,这也使得它成为实验动物中最重要的品系之一。
但是在这么多不同的应用中,你的C57BL/6、我的C57BL/6,真的一样吗?

(1)C57BL/6亚系小鼠的发展
目前,C57BL/6小鼠已经形成了两个主要亚系分支C57BL/6N和C57BL/6J,在全球形成约二十多种C57BL/6亚系小鼠。
由于不同供应商独立繁育的动物群体会随着时间的推移而发生遗传漂变,这些漂变可能导致表型的差异进而影响实验结果[2-6]。因此,在使用时要非常关注不同亚系间的命名和区别,也就是说,你的C57BL/6和我的C57BL/6,可能真的不一样!
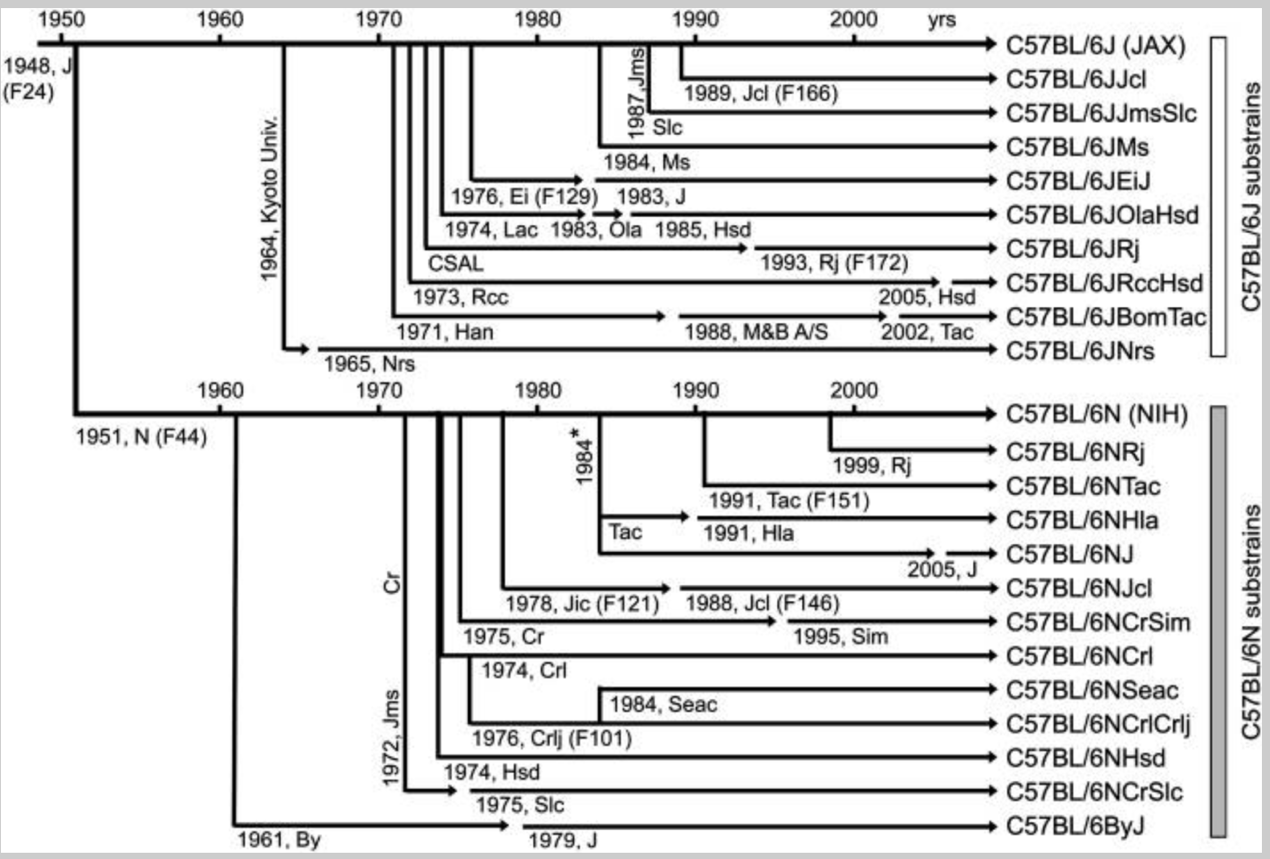
C57BL/6品系亚系图谱(7)

(2)C57BL/6亚系小鼠的区别
目前世界上已有约二十多种C57BL/6亚系小鼠,而不同亚系之间主要存在以下差异:
上文我们提到,目前世界上已有约二十多种C57BL/6亚系小鼠,而不同亚系之间又存在着差异。
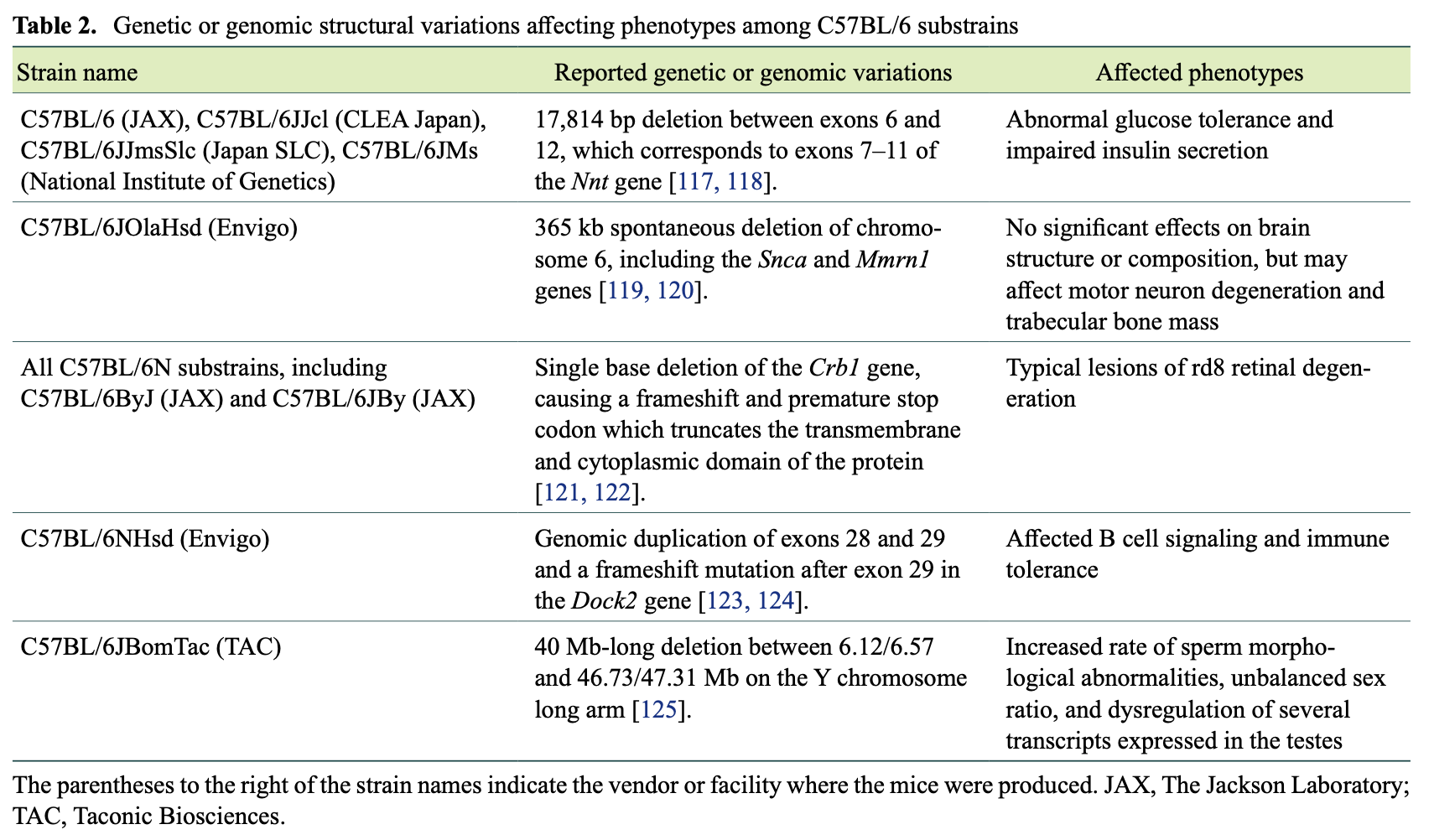
遗传或基因组结构的变异影响C57BL/6小鼠亚系的表型(7)
在了解相关基因突变后,我们还要清楚基因突变对表型的影响。有文献报道,不同C57BL/6亚系在行为学(好斗、筑巢)、神经系统(中风易感程度)、细胞表型(精子头部形态异常等)、酒精偏好等有区别[7]。
因此,根据C57BL/6小鼠亚系和表型的区别,再结合自身的研究领域,相信找到合适的研究对象就很容易啦。
既然不同供应商的C57BL/6亚系小鼠可能有基因和表型的区别,甚至会影响到实验,那要怎么鉴别C57BL/6小鼠呢,维通利华又是如何保持C57BL/6小鼠的“真身”呢?
接下来就一起探明C57BL/6小鼠的“真身”!

C57BL/6是近交系小鼠,维通利华采取同胞兄妹或亲子交配的方式保存,其后代基因纯合高,个体间遗传和表型趋于一致。同时,为了获得更高质量的后代,维通利华通常会在6月龄时淘汰种鼠,并且采用国际遗传学标准(IGS)来进行种群遗传管理,包括定期从美国Charles River引种核心种群、定期进行遗传检测等措施来消除地理隔离和基因污染的风险,采用金字塔繁育体系来确保动物的遗传背景清晰,持续为科研工作者提供质量稳定的实验动物,并且有清晰的遗传背景可以追溯C57BL/6小鼠的来源,让你清楚掌握C57BL/6小鼠的前世今生,拿下其“真身”!

C57BL/6小鼠可谓是货真价实的宝藏品系,是世界上最重要的品系之一,它有着强大的“诞生”背景和多种亚系,应用领域非常广泛,堪称啮齿类实验动物界最全能选手!
维通利华对保有的啮齿类实验动物品系均进行严格的遗传管理,确保C57BL/6JNifdc和C57BL/6NCrl小鼠的遗传背景清晰可溯源!
1、Waterston, R.H. et al. Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature. 2002;420:520-562
2、Bothe, G.W. et al. Genetic and behavioral differences among five inbred mouse strains commonly used in the production of transgenic and knockout mice. Genes Brain Behav.2004;3:149-157.
3、Bryant, C.D. et al., Behavioral differences among C57Bl/6 substrains: implications for transgenic and knockout studies. J Neurogenet. 2008;22:315-331.
4、Mulligan, M.K. et al. Alcohol trait and transcriptional genomic analysis of C57Bl/6 substrains. Genes Brain Behav. 2008;7:677-689.
5、Mekada, K. et al. Genetic differences among C57Bl/6 substrains.Exp. Anim. 2009;58:141-149
6、Zurita E. et al. Genetic polymorphisms among C57Bl/6 mouse inbred strains. Transgenic Res. 2011;20(3):481-489.
7、K. MEKADA, ET AL.Substrains matter in phenotyping of C57BL/6 mice.Exp Anim. 2021; 70(2): 145–160.
8、huang TT, Naeemuddin M, elchuri s, Yamaguchi M, Kozy HM, Carlson EJ, et al. Genetic modifiers of the phenotype of mice deficient in mitochondrial superoxide dismutase. Hum Mol Genet. 2006; 15: 1187–1194.
9、Toye aa, Lippiat Jd, Proks P, shimomura K, Bentley L, hu- gill a, et al. a genetic and physiological study of impaired glucose homeostasis control in C57BL/6J mice. diabetolo- gia. 2005; 48: 675–686.
10、Freeman hC, hugill a, dear NT, ashcroft FM, Cox Rd. de- letion of nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase: a new quantitive trait locus accounting for glucose intolerance in C57BL/6J mice. diabetes. 2006; 55: 2153–2156.
11、 asuni aa, hilton K, siskova Z, Lunnon K, Reynolds R, Perry VH, et al. Alpha-synuclein deficiency in the C57BL/6Jolahsd strain does not modify disease progression in the Me7-model of prion disease. Neuroscience. 2010; 165: 662–674.
12、Pelkonen a, Yavich L. Neuromuscular pathology in mice lacking alpha-synuclein. Neurosci Lett. 2011; 487: 350–353.
13、 Peña-oliver Y, Buchman VL, dalley JW, Robbins TW, schumann G, Ripley TL, et al. deletion of alpha-synuclein decreases impulsivity in mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2012; 11: 137–146.
14、Peña-oliver Y, sanchez-Roige s, stephens dN, Ripley TL. alpha-synuclein deletion decreases motor impulsivity but does not affect risky decision making in a mouse Gambling Task. Psychopharmacology
15、specht CG, schoepfer R. deletion of the alpha-synuclein lo- cus in a subpopulation of C57BL/6J inbred mice. BMC Neu- rosci. 2001; 2: 11.
16、Mattapallil, M.J. et al. The Rd8 mutation of the Crb1 gene is present in vendor lines of C57Bl/6N mice and embryonic stem cells, and confounds ocular induced mutant phenotypes. Invest. Ophthalmol.Vis. Sci. 2012;53(6):2921-2927.
17、Simon MM, Greenaway S, et al. A comparative phenotypic and genomic analysis of C57BL/6J and C57BL/6N mouse strains. Genome Biol. 2013 Jul 31;14(7):R82.
18、Mahajan Vs, demissie e, Mattoo h, Viswanadham V, Varki a, Morris R, et al. striking immune phenotypes in diverse gene-targeted mice are driven by a copy number variant orig- inating from a commercially available C57BL/6 strain. Cell Rep. 2016; 15: 1901–1909.
19、Wong SY, Coffre M, Ramanan D, Hines MJ, Gomez LE, Pe- ters La, et al. B cell defects observed in Nod2 knockout mice are a consequence of a Dock2 mutation frequently found in inbred strains. J immunol. 2018; 201: 1442–1451.